Enabling Efficient AI Workloads in Cloud-Native Development using Docker Offload
Cloud-native practitioners increasingly face the challenge of running modern machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) workloads on local machines that often lack the required CPU, memory or GPU resources. Docker Offload addresses this constraint by extending local development workflows to scalable, GPU-enabled cloud resources — all without leaving local development experience.
What is Docker Offload?
Docker Offload is a fully managed service that lets users execute Docker builds and run containers on the cloud infrastructure while not losing the local development experience. This drastically reduces the load on your local machine. It seems like magic behind the scenes as you will continue to run the same Docker commands with which you are familiar. However, Docker Desktop creates a secure SSH tunnel to a Docker daemon running in the cloud. It provides a local experience, even though the containers are created and workloads executed on the cloud infrastructure. Some of the key features include:
- Cloud-Based Builds: Offload complex container builds to high-performance, managed cloud runners.
- GPU Acceleration: Instantly access hardware needed for AI/ML pipelines without manual setup.
- Hybrid Workflows: Seamlessly transition between local and cloud execution with Docker Desktop or the CLI.
- VDI Compatibility: Supports environments like virtual desktops and machines without native virtualization support.
- Secure Communication: All traffic is secured, and ephemeral cloud environments are automatically cleaned up post-use.
Why use Docker Offload?
- Run containers that are compute-intensive and require more resources than your local machine
- Leverage cloud infrastructure for offloading heavy builds
- Ideal for high-velocity development workflows that need the flexibility of the cloud without sacrificing local development experience
- Instant access to GPU-powered environments
- Accelerate both development and testing without worrying about cloud infrastructure setup
- Develop efficiently in restricted environments like VDIs
Usage Model and Pricing
Developers receive 300 free GPU minutes during the beta. Afterward, usage is billed at $0.015 per GPU minute (subject to change post-beta). Sessions are ephemeral — resources are freed automatically after inactivity to optimize both cost and security.
Considerations
- Security: All remote sessions use encrypted tunnels. No data is retained after session termination, supporting both security and privacy best practices.
- Platform Neutrality: Docker Offload is vendor-agnostic and integrates with multiple cloud providers, ensuring a non-lock-in approach for practitioners.
- Community and Ecosystem: Docker Offload enhances existing workflows for AI, agentic application development and collaborative cloud-native projects, emphasizing standardization and compatibility with emerging AI orchestration frameworks.
How to Get Started?
Prerequisites:
- Docker Desktop 4.43.0 version or above
- Docker Hub Account with Docker Offload access
- Docker Offload is currently in beta, so you’ll need to sign up for access. Visit here to sign up for beta access.
- You will receive an email after which you can enable Docker Offload in your Docker Desktop.
- No restrictive proxy or firewall blocking traffic to Docker Cloud
How to Start Docker Offload
Once you receive access, you can enable Docker Offload in two ways: Either using Docker Desktop or via Terminal.
Start via Docker Desktop
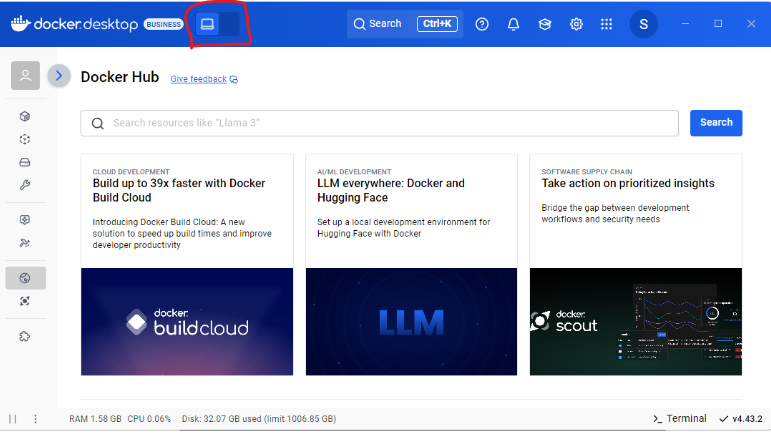
In the screenshot below, you can see a Toggle button at the top to enable Docker Offload.
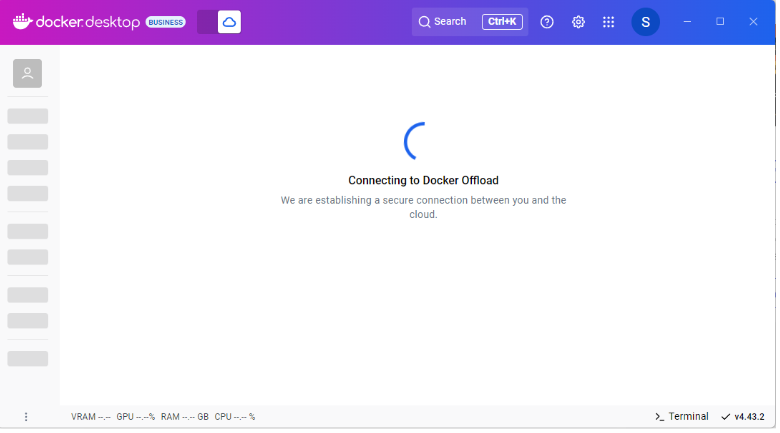
As soon as you do that, Docket Desktop color will change to purple and you’ll see a cloud icon in the header — which means that Docker Desktop is now securely connected to the cloud environment that mimics your local experience. Now, when you run builds or containers, they execute remotely but as a user you will not see any difference.
Start via Terminal
Open terminal and execute
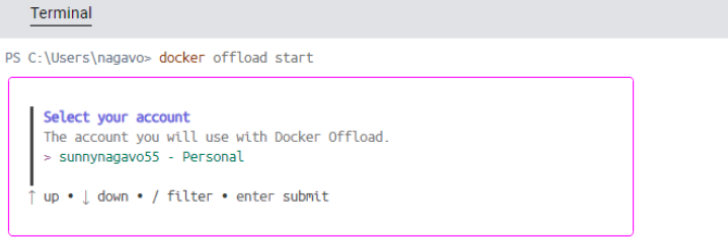
docker offload start
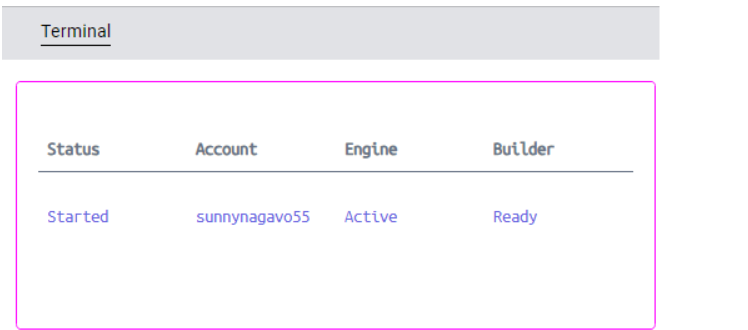
The command will display a prompt, as shown in the image below, allowing you to choose the account you wish to use for Docker Offload.
In the next prompt, it will ask whether you need GPU support.
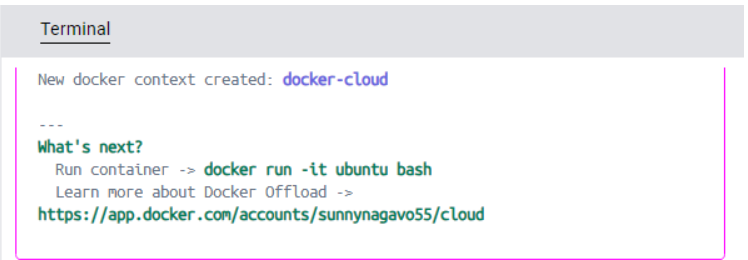
Once you select the options, it will display ‘New docker context created: docker-cloud’ message and the color of the Docker Desktop is changed to purple.
How to Run a Container With Docker Offload
Before running a container, make sure to verify Docker Offload is running properly. Execute the command below in the terminal to check the status.
docker offload status
You can also see a cloud icon with Offload + GPU running at the bottom left on your Docker Desktop window.
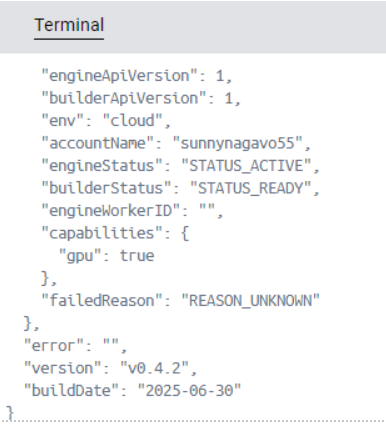
To get more information about Docker Offload status, run the command below which gives more details about daemon and status and if there were any failed reasons while running Docker Offload, as shown in the below screenshot.
docker offload diagnose
How to Build a Container With Docker Offload
For this article, I have forked a Docker Offload demo app from Docker GitHub Repo.
git clone https://github.com/sunnynagavo/docker-offload-demo.git
cd .\docker-offload-demo\
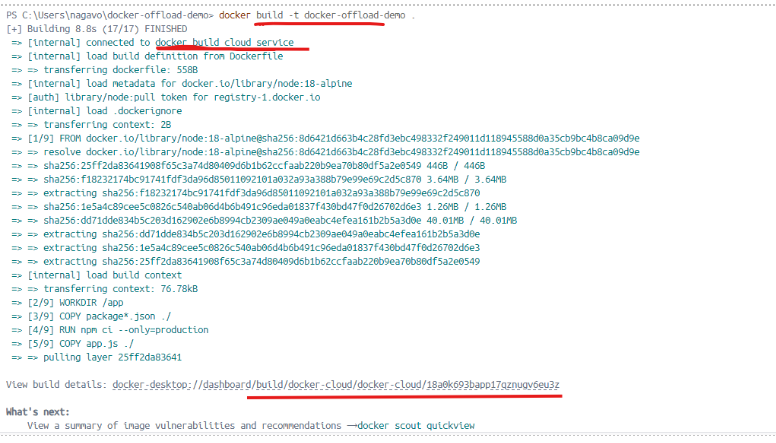
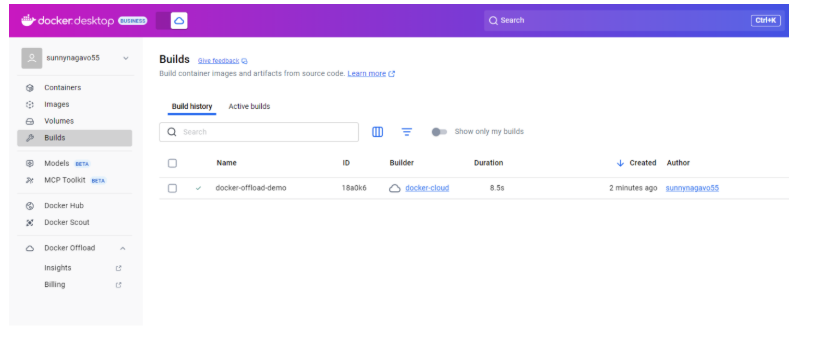
Once you are inside the folder, run the Docker Build command as shown below. The build will take place on cloud infrastructure rather than your local machine, which you can observe in the logs, as shown in the screenshot below.
You can also click on the Build tab on Docker Desktop to see the details of the build you just ran.
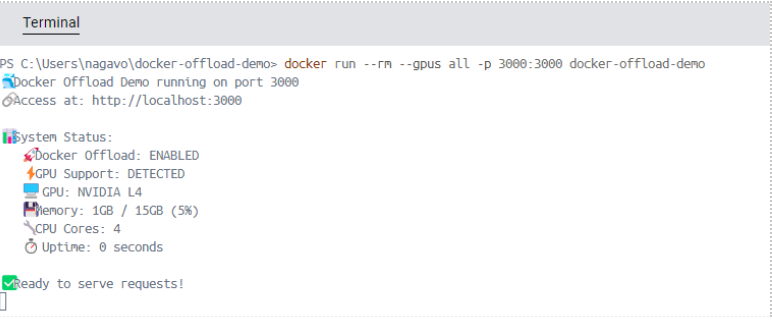
To run the application with GPUs, execute the below command in the terminal.
docker run –rm –gpus all -p 3000:3000 docker-offload-demo
You can see the output in the logs where it leveraged GPU (NVIDIA L4 by default) on the Docker cloud.
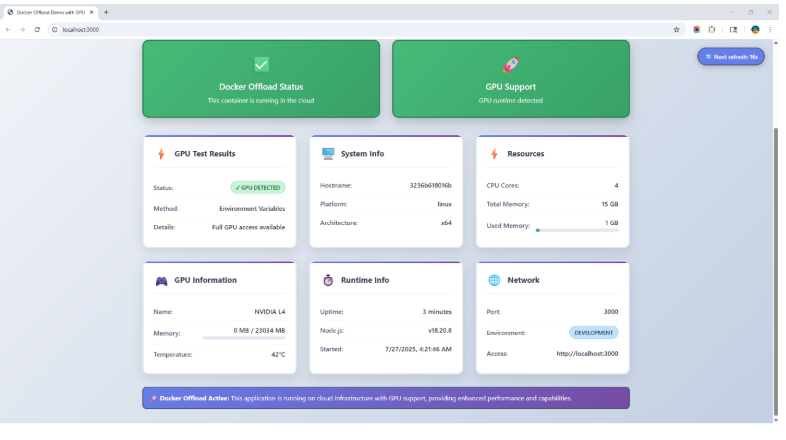
Navigate to the URL http://localhost:3000 to see the demo application as shown in the below screenshot.
The demo application shows a comprehensive view of your system’s performance by providing confirmation that you are utilizing Docker Offload. The app clearly shows the stats about what GPU hardware (NVIDIA L4) is used in running along with resources used in running the application.
How to Stop Docker Offload
Just like starting Docker Offload, there are two ways to stop Docker Offload.
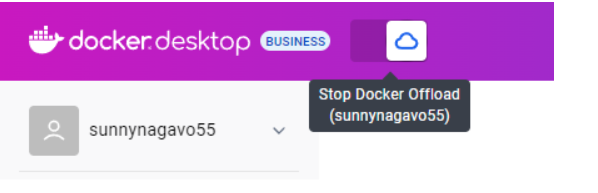
Stop via Docker Desktop
You can use the same toggle button at the top to stop Docker Offload and color changes back to your original theme.
Stop via Terminal
Open Terminal and execute the below command to stop Docker Offload.
docker offload stop
Once it’s stopped, all the previously built images and containers will be cleaned. By running the above commands, you will now be able to build images and run containers locally.
Conclusion
Docker offload closes the gap between ease of local development and the power of cloud scalability. It helps developers to run compute-intensive workloads in the cloud without losing the experience of working locally. Docker Offload is like adding a supercomputer brain to your local machine. I highly encourage developers to experience the power of Docker Offload. So, what are you waiting for? Go ahead and submit your request for access to Docker Offload.
For more details, check out Docker official documentation on Docker Offload.