Unleashing the Power of Argo CD by Streamlining Kubernetes Deployments
Kubernetes has been around for over a decade, and its application has been rising ever since. Started in 2014 by Google, Kubernetes (K8s) is an open-source container orchestration system that automates software deployment, scaling and management. Initially developed by Google, it was transferred to the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), which maintains and develops it with a community of 80K+ contributors. It provides seamless deployments, but to ensure consistent and automated delivery of new code versions — from development to production — without manual intervention, we need continuous delivery (CD) in Kubernetes.
There are many CD tools for Kubernetes on the market, but the popular ones include Argo CD, Flux CD, Jenkins X and GitHub Actions. Among them, Argo CD has become a popular choice for big enterprises because of its declarative and version control system. According to the official docs:
Argo CD is a Declarative GitOps CD Tool for Kubernetes
Application definitions, configurations and environments are declarative, and application deployment and life cycle management are automated and easy to understand, which makes Argo CD an ideal choice for many companies.
How Does Argo CD Work?
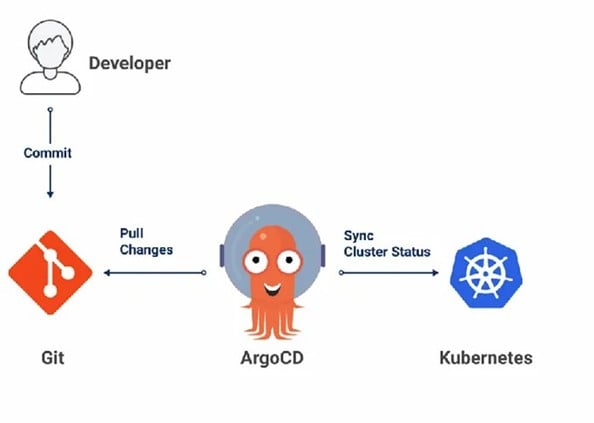
Argo CD follows the GitOps pattern. It uses Git repositories as the source of truth for defining the desired application state. It provides various options to describe our Kubernetes manifest:
- Kustomize Applications
- Helm Charts
- Jsonnet Files
- Plain, direct YAML/JSON manifests
- Any custom config management tool configured as a config management plug-in
It automates an application’s desired state in the specified target environments. You can track your applications’ deployments with branches and tags or be pinned to a specific version of manifests at a Git commit.
Argo CD is implemented as a Kubernetes Controller that continuously monitors running applications and compares the current state with the desired state (as specified in the Git repository). The configuration in the Git repo is the single source of truth. When the desired state differs from the current state, the application is OutOfSync. To address this, Argo CD reports and visualizes the differences while providing facilities to sync the live state back automatically or manually to the desired target state. Any modifications in the Git repo will change the desired state of the application.
Push- vs. Pull-Based CI/CD
Earlier continuous integration (CI) and CD implementations relied on push-driven behavior, which connects your cluster to your CI/CD platform and uses tools such as kubectl and Helm within your pipeline to apply Kubernetes changes.
Argo CD is a pull-based CI/CD system. It runs inside your Kubernetes cluster and pulls sources from your repositories. Argo then applies the changes for you without a manually configured pipeline.
This model is more secure than push-based workflows. You don’t have to expose your cluster’s application programming interface (API) server or store Kubernetes credentials in your CI/CD platform. Compromising a source repository only gives an attacker access to your code instead of the code and a route to your live deployments.
Components
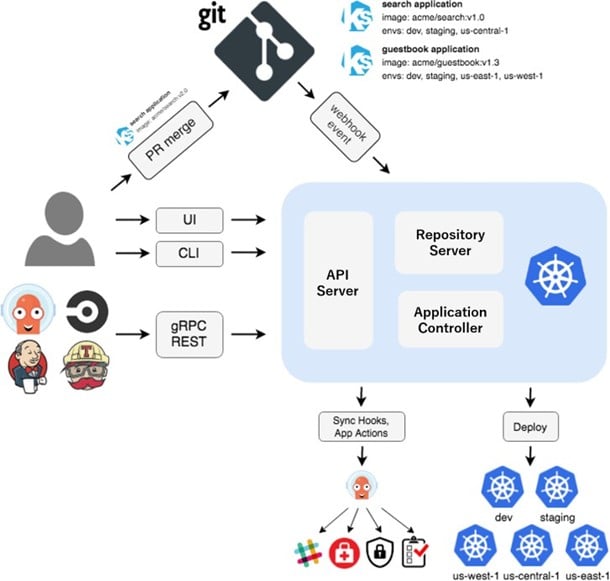
Argo CD has three components: API Server, Repository Server and Application Controller. Each plays a crucial role; if any fails, the application will fail. Let us understand them in depth:
API Server: The API server is a gRPC/REST server that exposes the API consumed by the web user interface (UI), command line interface (CLI) and CI/CD system. It has the following duties:
- Application management and status reporting
- Involving application operations (e.g., sync, rollbacks)
- Repo and cluster management
- Auth and its external identity provider
- Role-based access control (RBAC) enforcement
- Listener to webhooks of Git
Repository Server: It is an internal server that maintains a local cache of the Git repo holding the application manifest. Primary responsibilities include generating and returning Kubernetes manifests when provided with the following inputs:
- Repo URL
- Revision (commit, tag, branch)
- Application path
- Template-specific settings: parameters, helm values.yaml
Application Controller: A Kubernetes Controller continuously monitors running applications and compares the current state with the desired state (as specified in the Git repo). It detects the OutOfSync application state and optionally takes corrective measures. It is primarily responsible for invoking user-defined hooks for life cycle events, including pre-sync, sync and post-sync.
Challenges With Continuous Delivery
Argo CD combats several CD challenges by implementing a GitOps approach for deployments. It automates deployment by managing continuous drifts, simplifying operations and ensuring more consistent and reliable releases. The following are some key challenges solved by Argo CD:
- Configuration Drift: Argo CD ensures that deployments reflect the desired state of the application defined in Git (the single source of truth) and prevents misconfiguration within the cluster.
- Automation and Reliability: It automates deployments by eliminating manual steps and reducing errors.
- Consistency and Reliability: Using Git as the source code, it ensures consistent deployment across environments, improving reliability.
- Multi-Cluster Management: It supports multi-cluster management by streamlining deployment across many Kubernetes clusters in distributed environments.
- Simplified Operations: It simplifies operations by providing a user-friendly interface and automating tasks like rollbacks with just one click.
Argo CD Features
Automated deployment of applications to specified target environments
- Support for multiple config management/templating tools (Kustomize, Helm, Jsonnet, plain YAML)
- Ability to manage and deploy to various clusters
- Multi-tenancy and RBAC policies for authorization
- Rollback/Roll-anywhere to any application configuration committed in the Git repository
- Automated or manual syncing of applications to their desired state
- Web UI that provides a real-time view of application activity
- CLI for automation and CI integration; Webhook integration (GitHub, BitBucket, GitLab)
- Access tokens for automation
- Audit trails for application events and API calls
- Prometheus metrics Parameter overrides for overriding Helm parameters in Git
Case Studies
How do big enterprises such as loveholidays, CVTE and Babylon leverage Argo CD to enhance productivity?
Argo CD was accepted into the CNCF on March 26, 2020, at the incubating maturity level, and then moved to the graduated maturity level on December 6, 2022. It has helped many companies — such as loveholidays and CVTE — run workflows, manage clusters and implement GitOps correctly.
loveholidays is one of the fastest-growing online travel agencies in the UK and Ireland. It expanded to the German market in 2023 to offer its customers unlimited choices with unmatched ease and unmissable value — providing the perfect holiday experience. As their user base increased, they found improving overall observability and incident detection difficult. To solve this, loveholidays adopted Linkerd as its Kubernetes service mesh, along with Argo CD for GitOps and Argo Rollouts for powering canary deployments. By the numbers, loveholidays handles trillions of hotel and flight combinations per day, deploys over 1,500+ production deployments per month and runs around 5,000 pods in production with around 300 deployments/StatefulSets. Recently, it migrated from Flux to Argo CD, and with GitOps-powered deployments, it deployed over 1,500 times to production in a month.
CVTE, based in China, is an electronic company that embraced cloud-native tech and has been running services on Kubernetes for years. Most of their applications run on bare metal and edge clusters in a private environment, making access to these applications outside the cluster challenging. To solve this, they used OpenELB, which exposed the load balancer services on bare metal using Layer 2 mode. They use Argo CD to build automated pipelines and NGINX Ingress to handle Layer 7 requests. In their domain, when someone visits argocd.cvte.com, the system forwards the request to the router, which broadcasts the request. By using Argo CD and OpenELB, the company has reduced the complexity of its infrastructure, enhanced its self-healing capabilities and improved its monitoring capabilities.
Babylon, a UK startup launched in 2013, has helped to revolutionize medical services and reduce the waiting time for doctors’ appointments from weeks or even two to mere minutes or hours.
Their products leverage machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI), and there was insufficient power in-house to run the services. To solve that issue, they migrated their user-facing application to a Kubernetes platform in 2018 using Kubeflow, and the change has been incredible! Teams can get access instantaneously instead of waiting hours or days to compute. Clinical validation, which used to take 10 hours, is now done in under 20 minutes. Using Argo CD for GitOps, the team can scale the process massively.
Best Practices for Using Argo CD
Here are some of the best practices to keep in mind when working with Argo CD:
- Use ApplicationSets for Dynamic App Management: Leverage ApplicationSets to automate the deployment of similar apps (e.g., per tenant or cluster) from templates, reducing boilerplate and manual interventions.
- Pin Argo CD Versions and CRDs: Avoid auto-upgrading Argo CD or its custom resource definitions; pin versions explicitly to avoid breaking changes or unexpected behavior in the app.
- Apply Resource Exclusions and Ignore Differences: Configure resource exclusions or diff settings (e.g., ignore status fields) to prevent false-positive drift detections.
- Tag and Label Applications for Automation and Auditing: Use consistent metadata on your Argo CD apps to enable automated filtering, reporting or life cycle management.
- Run Argo CD in a Dedicated Namespace or Cluster: Isolate Argo CD to a specific namespace or cluster to simplify access control, avoid conflicts and improve operational clarity.
A Practical Demonstration
After learning about Argo CD and its applications, let us have a hands-on demo to see how it works. We will install Argo CD in a minikube cluster and witness the magic. Follow the steps below:
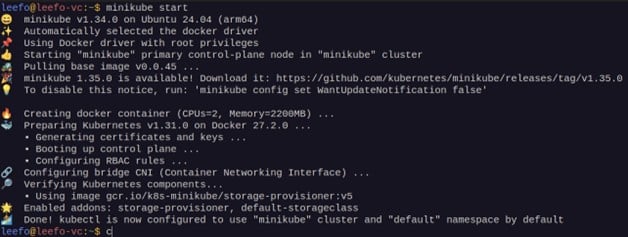
- If you don’t have minikube installed, install it from its official website and run the following command:
minikube start
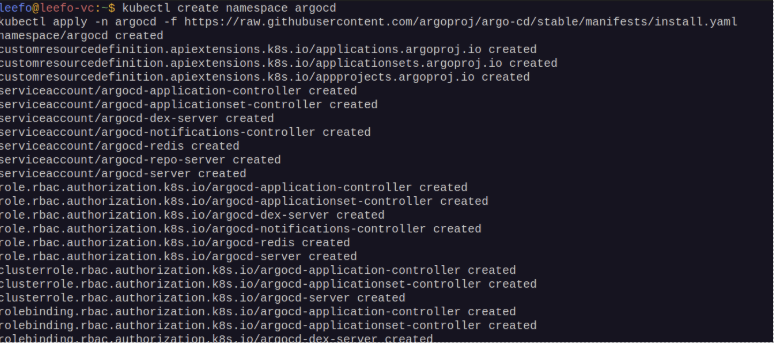
- Install Argo CD using the following command: kubectl create namespace
- argocd
kubectl apply –n argocd -f
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
- Get the initial password using the following command:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath='{.data.password}’ | base64 -d
Copy the output and save it for the next step.
Expose the Argo CD API server using port forwarding: kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8081:443
Now, go to localhost:8081. A warning will be displayed — accept the risk and continue.
In the Username field, enter ‘admin’; the password is the saved output from the previous step.
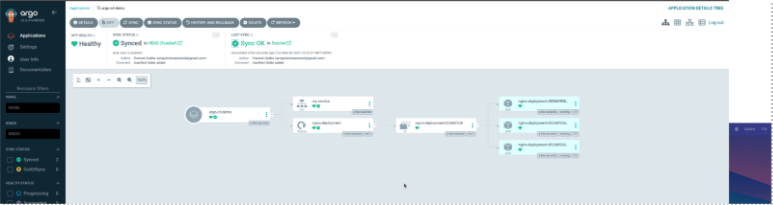
After providing the credentials, you will be presented with the Argo CD dashboard. Click on ‘Create Application’ and provide the following configuration:
- Application Name: argo-cd-demo
- Project Name: default
- Sync Policy: Automatic
Under Source, provide the following configuration:
- Repository URL: https://github.com/rajudandigam/argocd-demo.git
(You can also fork the repository and use your own GitHub account — it may be more convenient.)
- Revision: Head
- Path: manifests
Under Destination, provide the following configuration:
- Cluster URL: https://kubernetes.default.svc
- Namespace: default
Then, click ‘Create’. Wait for two to three minutes for the pods to become healthy.
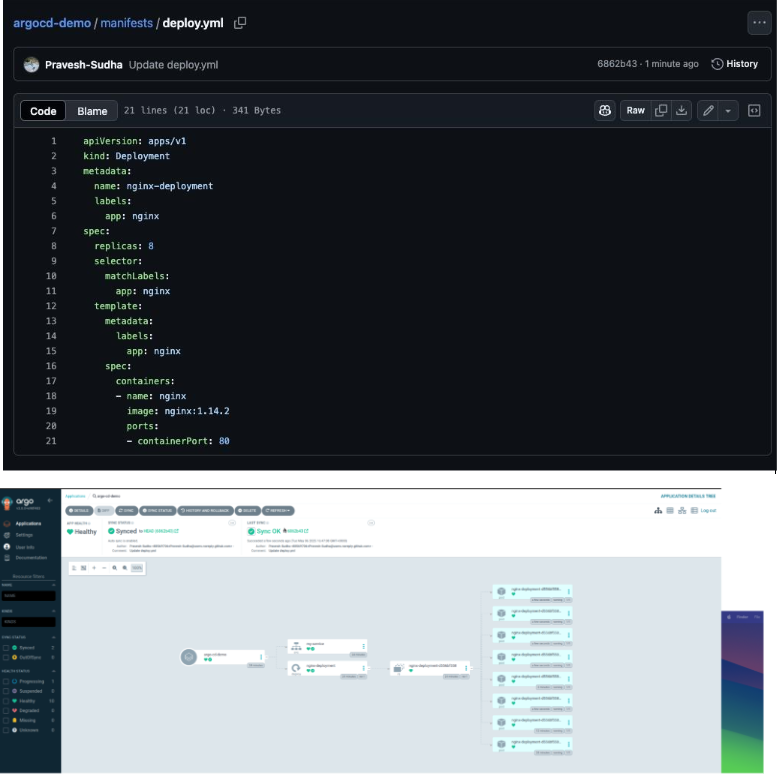
Now, in the terminal, run the following command to change the number of replicas of nginx-deployment:
kubectl scale –replicas=2 deployment/nginx-deployment
You will notice that the number of pods increases to two, and the application’s status becomes OutOfSync. However, once you click ‘Sync’, it will automatically revert to the previous version, as defined in our Git repository, where we specified three replicas. You can enable self-healing to perform this task automatically.
Since our Sync Policy is set to automatic, let’s make a change in the Git repository and see if it reflects in the application. In the deploy.yml file, change the number of replicas from three to eight and commit the change. After a few seconds, you will see that Argo CD pulls and applies the changes to the application.
Once you are done, just run the following command to clean up the resources: minikube delete
References
Key Takeaways
- Argo CD (the de facto CD tool for Kubernetes) makes deployment releases smooth by using Git as a single source of truth. You can define your app’s state in Git, and Argo CD will keep the cluster in the desired state.
- Unlike the traditional push–based approach, Argo CD runs inside the cluster and pulls changes from Git, which ensures that API keys and secrets are not exposed, making it a safer and more reliable choice for big enterprises.
- Big enterprises such as loveholidays and CVTE adopted Argo CD to handle massive-scale deployments. loveholidays, for example, handles trillions of requests and 1,500+ deployments per month, all thanks to Argo CD.
- Argo CD addresses core continuous delivery challenges such as configuration drift, automated deployment workflows and multi-cluster application consistency. It ensures consistency across environments and lets you roll back to the previous version with just one click, reducing error and stress.
- This blog includes a hands-on demo that shows how easy it is to set up Argo CD on a minikube cluster and watch it sync changes in real time.